Fiber is an essential component of a balanced diet, and its significance becomes even more pronounced when following a ketogenic (keto) diet. Characterized by high fat and low carbohydrate intake, the keto diet often leads to a reduction in fiber-rich foods, which can impact overall health.
While the primary focus of keto is to induce ketosis—a metabolic state where the body burns fat for fuel—fiber plays a crucial role in maintaining digestive health, regulating blood sugar levels, and supporting weight management.
Incorporating adequate fiber into a keto diet can help mitigate common side effects like constipation and digestive discomfort, which are often experienced due to the reduced intake of traditional fiber sources. As discussed in https://www.drberg.com/blog, fiber—classified into soluble and insoluble types—not only aids digestion and stabilizes blood sugar but also plays a crucial role in maintaining gut health and supporting long-term wellness, even when following a low-carbohydrate lifestyle.
Understanding the Role of Fiber in a Keto Diet
Fiber serves multiple roles in a keto diet:
- Promoting digestive health: With reduced intake of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, many keto dieters miss out on fiber, leading to gastrointestinal issues like constipation and bloating.
- Enhancing satiety: High-fiber foods help individuals feel full longer, which aids in reducing overall calorie intake—a key component of successful weight management.
Incorporating fiber into a keto meal plan can improve satisfaction and make the diet more sustainable long term.
How Fiber Supports Digestive Health on a Keto Diet
The relationship between fiber and digestive health is well-documented and highly relevant to keto followers:
- Regular bowel movements: Fiber bulks up stool and promotes regularity, preventing constipation.
- Gut microbiome support: Fiber fosters the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, essential for nutrient absorption, immune function, and mental health.
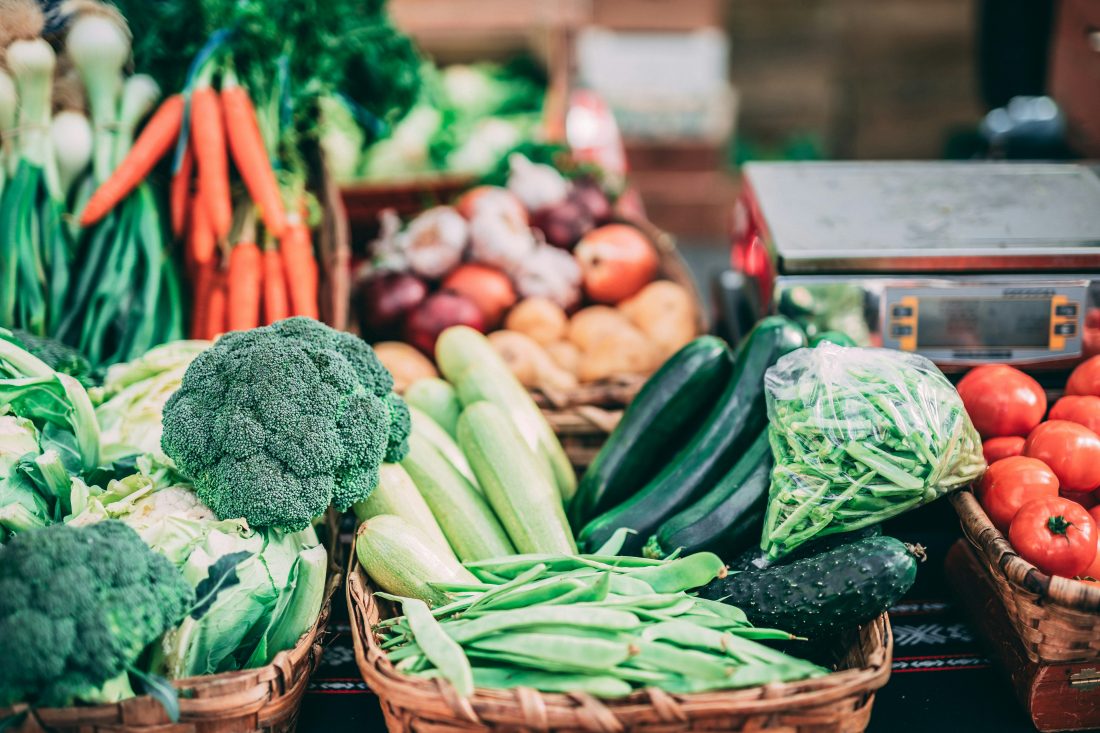
Including high-fiber, low-carb foods like leafy greens, avocados, nuts, and seeds helps maintain a diverse and healthy gut microbiome, enhancing both digestive and overall health.
The Impact of Fiber on Blood Sugar Levels in a Keto Diet
Fiber plays a key role in regulating blood sugar levels:
- Slowing sugar absorption: Soluble fiber slows glucose entry into the bloodstream, promoting stable blood sugar levels.
- Supporting insulin sensitivity: Stable blood sugar control is especially critical for those with insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes.
Incorporating fiber-rich foods like chia seeds and flaxseeds aligns with keto principles while supporting metabolic health.
Incorporating High-Fiber Foods into a Keto Meal Plan
Strategic planning makes it easy to incorporate high-fiber foods into a keto meal plan:
- Leafy greens: Spinach, kale, and other greens are low in carbs but high in fiber.
- Cruciferous vegetables: Broccoli and cauliflower provide fiber and essential nutrients.
- Nuts and seeds: Almonds, chia seeds, and flaxseeds add fiber and healthy fats.
Choosing these foods ensures that fiber intake remains high without compromising ketosis.
The Relationship Between Fiber and Weight Management on a Keto Diet
Fiber’s Crucial Role in Keto Weight Management
Supported by research, Fiber-rich foods support weight management by enhancing satiety and regulating hunger:
- Appetite regulation: Fiber influences hunger hormones like ghrelin and leptin, promoting feelings of fullness.
- Larger meal volume: Fiber allows for more substantial meal portions without a significant increase in calories.
Fiber’s Dual Benefits for Keto Dieters
Incorporating high-fiber foods not only aids digestion but also helps individuals control their appetite, making weight management on a keto diet more achievable.
Addressing Common Misconceptions About Fiber and Ketosis
Several misconceptions about fiber and ketosis need clarification:
- Not all carbs are equal: Fiber does not raise blood sugar like digestible carbohydrates do, and it should not be eliminated.
- High-fiber foods fit keto: Many fiber-rich foods are low in net carbs and perfectly compatible with a ketogenic lifestyle.
Understanding these nuances allows individuals to maintain ketosis while benefiting from fiber’s health-promoting properties.
Tips for Increasing Fiber Intake While Following a Keto Diet
Practical strategies for boosting fiber on a keto diet include:
- Prioritize low-carb vegetables: Spinach, zucchini, asparagus, and bell peppers offer fiber and micronutrients.
- Incorporate nuts and seeds: Snack on almonds or add chia and flaxseeds to meals for a fiber boost.
- Use alternative flours: Almond flour and coconut flour add fiber to keto baking.
- Stay hydrated: Adequate water intake aids fiber digestion and prevents discomfort.
By implementing these strategies, individuals can successfully increase their fiber intake and enjoy the full benefits of a keto diet.